Development of Moral Autonomy
What are the observable impacts of problem situations analyses and discussions in the development of learners' moral autonomy?
General topic of interest
The main idea of this project is to understand the development of learner’s moral autonomy after watching and discussing videos with different conflicts and problem situations.
During my last almost ten years working with education, I was always interested in observing how learners grow and develop their sense of justice, dignity, fairness, rightness, among other moral senses that we all develop in different, individual or collective ways. Studies from Yves de la Taille and Piaget about moral development and moral autonomy were fundamental for my own tragectory as an educator.
Participants
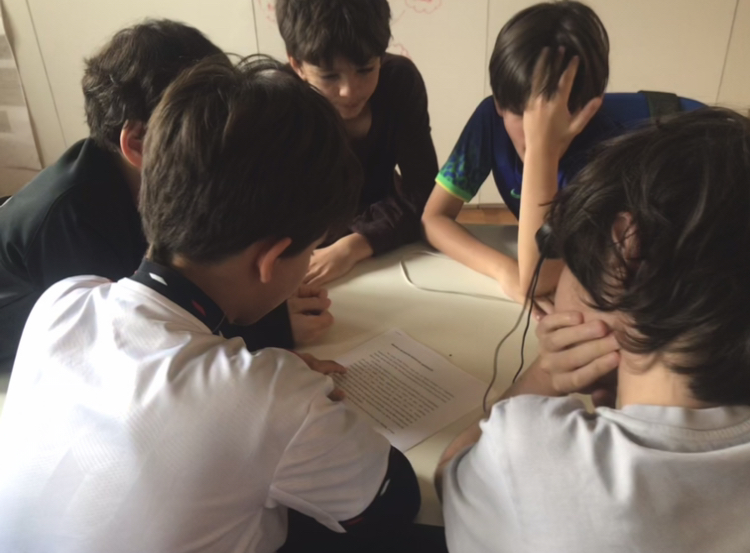
The research gathered data collected with the help of a Grade 5 group of a private Project Based Learning school in the city of São Paulo, state of São Paulo, in Brazil. The researched group is formed by 18 students, from 10 to 11 years old. Among the students of the group there are 6 girls and 12 boys. Most of the learners have been studying in the researched school since they were around 7 years old, yet they have been through different groupings. In addition to the changes in the formation of the groups, it is also crucial to consider that during two years (in 3rd and 4th grades) the students have faced, together with people all over the world, the pandemic situation due to Covid-19.
Literature Review
“Moral autonomy appears when the mind regards as necessary an ideal that is independent of all external pressures.”
Jean Piaget
Data collecting approach
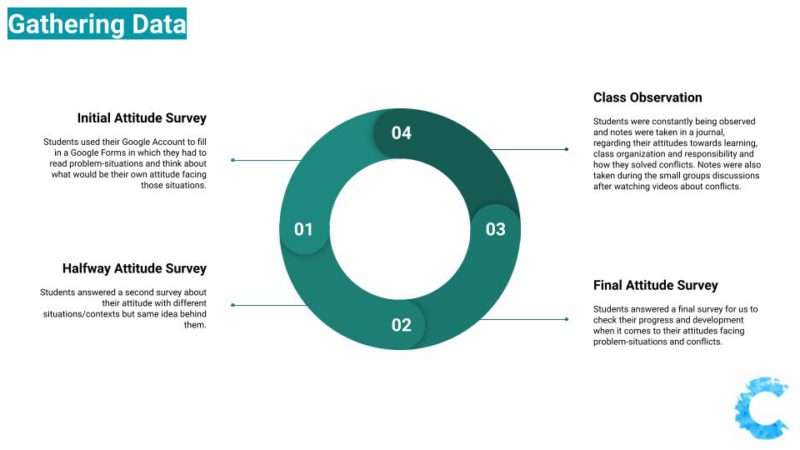
We used pre and post surveys to compare 5th graders responses before watching and discussing videos about conflicts resolutions and after.
Data collection tools/resources
For our surveys we used Google Forms as the main tool.
Emerging results
First Survey: Avoiding Responsibility
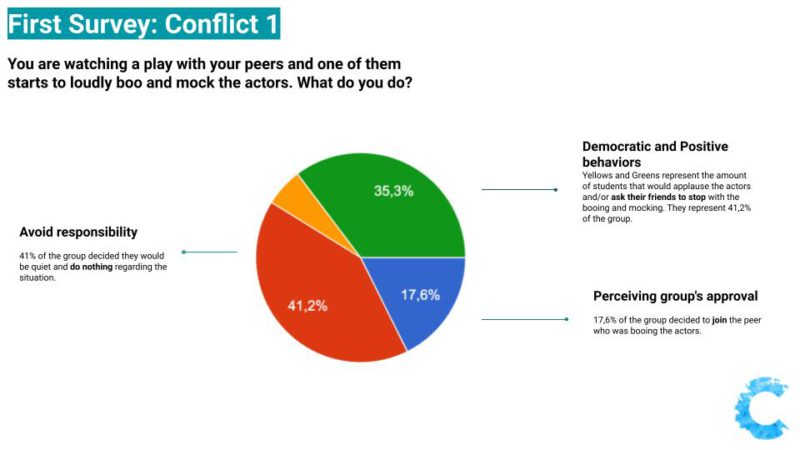
In our first survey, before discussing and watching videos about conflicts resolutions and problem situations with the learners, in most of the questions, there were students following the bad attitude or avoiding responsibility and not taking any attitude towards injustice.
In 5 out of 6 questions, there were from 2 to 3 learners deciding to follow the bad attitude and join their peers.
These learners choosing the "misbehavior" or "disrespectful" attitude were not always the same, which also called our attention. Out of 18 students, 8 of them choose an undesired attitude at least once.
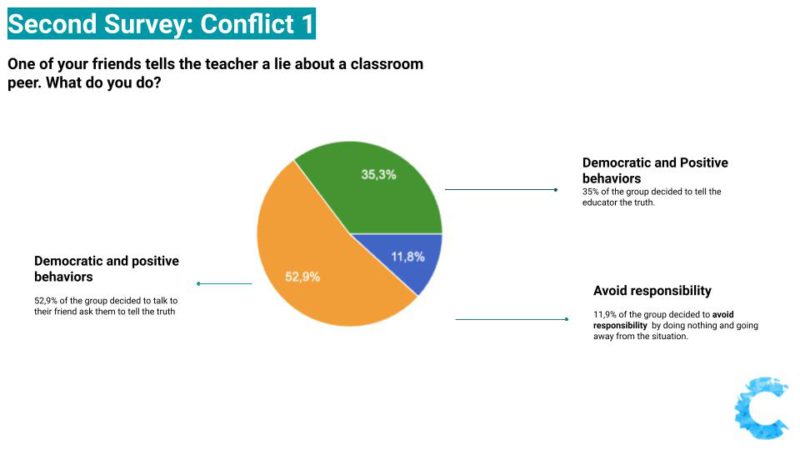
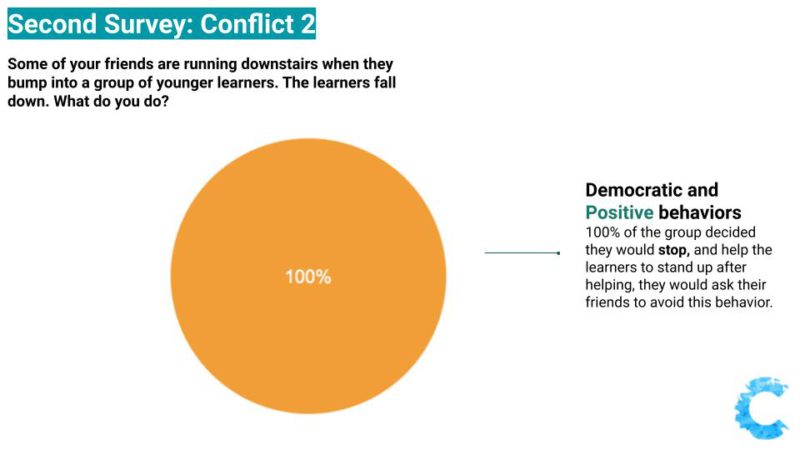
Second Survey: Avoiding Responsibility except when it involves younger students
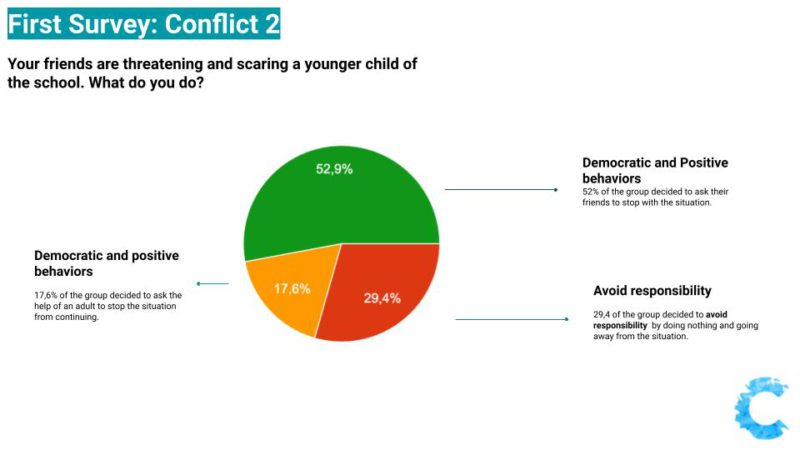
It is possible to observe in their final responses, that learners continued to avoid responsibility in most of the situations. In some questions, over 6 students out of the 18 answers, decided to "do nothing" while facing a situation involving unfairness in which one person was suffering with consequences. One highlight was that in the situation involving younger learners, all the students took responsibility and decided they would do something to help and stop the unjustice to continue.
Reflections
Out of this study, it was possible to observe, during the talks and conversations, that students started with really fixed ideas about what was the meaning of fairness, justice and so on, and while discussing and talking about the present videos, they were able to expand their ideas and, sometimes, change their minds. At one point, a learner who was strongly saying it was fair to do some paperwork for a friend if they were your friend, but wasn't fair to do it for a peer who wasn't your friend, finally had an insight and while the group was already discussing something else he said: "No, wait! It isn't fair to do double work for someone just because they are your friends, unless they have a good reason not to do it...".
A second conclusion is that a work to develop learner's moral autonomy needs more time and more consistency. Which is why I intend on continuing this same research next year with the next group to come, with more consistency, frequency and data.